Describe the Structure of the Heart
Coverings of heart - Pericardium square6 Double walled fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and great vessels. It is a four-chambered muscular organ protected by a double walled membranous sac pericardium.
Chambers and Circulation through the Heart.
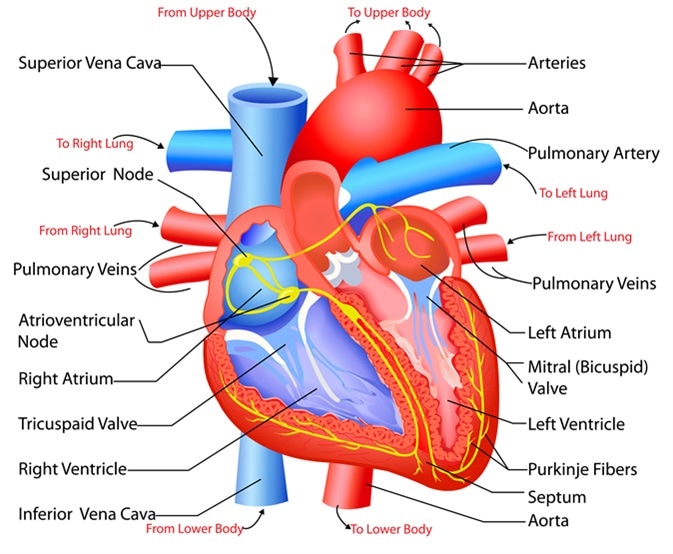
. 676 Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Papillary muscles Tricuspid valve Right atrium Pulmonary. The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity medially between the lungs in the space. The inner wall of the heart has a lining called the endocardium.
The upper two chambers are called right and left atrium. The shape of the heart is similar to a pinecone rather broad at the superior surface and. Human heart is four chambered.
The two layers have a potential space or cavity in between them the pericardial cavity which consists of about 50 ml of pericardial fluid. The inner layer of the heart wall is called endocardium. Prevents blood movement from right ventricle to right atrium.
The lower two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. A describe the structure and functions of the heart. It is situated in the thoracic cavity in between the lungs slightly tilted to the left.
Structure and function of the heart Structure and function of the heart Structure and function of the heart Rev Esp Cardiol. Apex is the tapered inferior end tilts to the left. The human heart is a mesodermally derived hollow muscular organ.
The middle layer of the heart wall is called myocardium. Recall that the hearts contraction cycle follows a dual pattern of circulationthe pulmonary lungsand systemic body circuitsbecause of the pairs of chambers that pump blood into the circulation. Relate the structural and functional characteristics of cardiac muscle cells.
Inelastic Protects the heart from sudden overfilling Pierced superiorly by the aorta SVC. The heart is composed of three layers. Structure from which chord tendineae originate.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of. Inside Our Earth Perimeter and Area Winds Storms and CyclonesStruggles for Equality The Triangle and Its Properties. Describe the structure and functions of the heart skeleton.
Shape and Size of the Heart. And the lower two chambers are called the right and left ventricle. The heart contains four inner chambers.
The epicardium the myocardium and the endocardium illustrated in Figure 1. Double-layered membrane around heart. The chambers are separated by a septum.
This preview shows page 5 - 8 out of 100 pages. Prevents blood movement from left ventricle to left atrium. From the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery or aorta.
Square6 Superficial layer-Fibrous pericardium. Internal Structure of the Heart. The walls and lining of the pericardial cavity are made up of a membrane known as the pericardium.
Article in Spanish Author F Torrent-Guasp 1 Affiliation. In order to develop a more precise understanding of cardiac function it is first necessary to explore the internal anatomical structures in more detail. Wide at base 5 in.
The heart has four chambers The right atrium- receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle The right ventricle- receives the blood from the atrium and pumps it to the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs. The depression among it and the heart is loaded up with pericardial liquid which lessens grinding between the sac and thumping heart. The pericardium is a fibre membrane found as an external covering around the heart.
Structure of the heart The heart can be found at the chests center underneath the sternum in a thoracic compartment. The heart is a 4-chambered pump that lies in the thoracic cavity within the mediastinumThe Base is the wide superior portion of heart large vessels attach here. Learn about the anatomy of the heart in this guide.
The outer layer of the heart wall is called epicardium. The heart is enclosed in a tough two-layered sac the pericardium comprising inner visceral pericardium attached to the heart and the outer parietal pericardium. One-way valves separate the four chambers.
Mensuration Factorisation Linear Equations in One VariableUnderstanding Quadrilaterals The Making of. Heart Anatomy Location of the Heart. The atria plural of atrium are where the blood collects when it enters the heart.
In humans the heart is about the size of a clenched fist and it is divided into four chambers. Gives rise to left and right pulmonary arteries. Two atria and two ventricles.
The two upper thin-walled chambers Auricle or Atria and the lower thick-walled chambers ventricles. Climate Vegetation and Wildlife. Its encased in an intense membranous sac called the pericardium.
The heart wall is made up of three layers. It is located in the. The myocardium consists of the heart muscle cells that make up.
Large blood vessels leave and enter the heart and help to keep it in position. Internal structure of the heart. Weighs 10 ounces 35 in.
From base to apex. The heart is primarily made of a thick muscle layer called the myocardium surrounded by membranes. The upper two chambers of the heart are called auricles.
Each side of the heart consists of an atrium and a ventricle which are two connected chambers. The human heart is situated to the left of the chest and is enclosed within a fluid-filled cavity described as the pericardial cavity. The human heart is four-chambered.
The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein. Maps Practical Geometry Separation of SubstancesPlaying With Numbers India. The two auricles are separated by an interatrial septum and the two ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum.
The size of the heart is about the clenched fist. The heart has two atria that fill in as accepting chambers and two ventricles that fill in as siphoning chambers. Structure of human heart the human heart is divided into four chambers.
The left atrium- receives blood from the lungs pulmonary veins oxygenated blood The left ventricle- receives blood from the left. It comprises four chambers and several valves that regulate the normal flow.

Blausen 0456 Heart Posterior Heart Wikipedia Heart Anatomy Home Health Remedies Anatomy

Http Www Aviva Co Uk Library Images Med Encyclopedia Cfhg350strhea 002 Gif Heart Structure Human Anatomy And Physiology Cardiovascular System

Learn How The Heart Beats In The Phases Of The Cardiac Cycle Anatomia Del Corazon Valvulas Cardiacas Anatomia Y Fisiologia Humana

Conduction System Of The Heart Heart Diagram Cardiac Cycle Anatomy And Physiology

11 The Heart Is An Organ In The Circulatory System Human Heart Anatomy Heart Anatomy Human Circulatory System

3d Heart Anatomy Animation Heart Anatomy Heart Diagram Anatomy

Structure And Function Of The Heart

Anterior And Posterior View Of Heart Human Anatomy Picture Cardiac Anatomy Human Heart Anatomy

Pin On Human Anatomy Structure Physiology

Knowledge Of The Structure And Function Of Heart Definition Examples Diagrams

Explain The Structure And Function Of The Heart Structure And Function Life Science

Simple Heart Diagram Simple Heart Diagram Labeled Human Heart Diagram Human Heart Diagram Human Heart Anatomy Simple Heart Diagram

8 Warning Signs That Your Heart Does Not Work Properly Seewhat Human Heart Diagram Heart Diagram Human Heart

Heart And Great Vessels Anterior View The Heart Is Enclosed In The Pericardial Sac The Innermost Layer Of W Heart Structure Cardiovascular System Emt Study
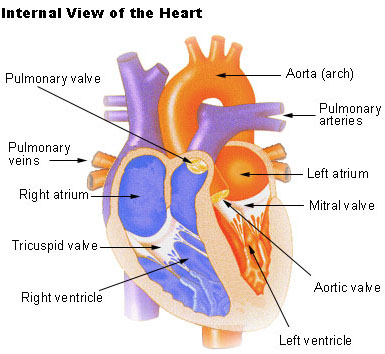
Seer Training Structure Of The Heart

Gcse Biology The Heart Youtube An Overview On The Structure And Function Of The Heart If You Have Any Questions O Heart Structure Biology Diagrams Biology




Comments
Post a Comment